| This project from the UF/IFAS Citrus Research and Education Center (CREC) is surveying citrus groves across the state to see how quickly the trees recover from Hurricane Ian. Our last update discussed the impact of Huanglongbing (HLB), a bacterial disease, on fruit production. HLB puts trees at a disadvantage health-wise and production-wise. This makes it even harder for them to recover after damage from events like hurricanes. This update discusses how trees are recovering over 10 months after the hurricane. Though the trees may look healthy this far out from the hurricane, they are still recovering and exhibiting signs of stress. |
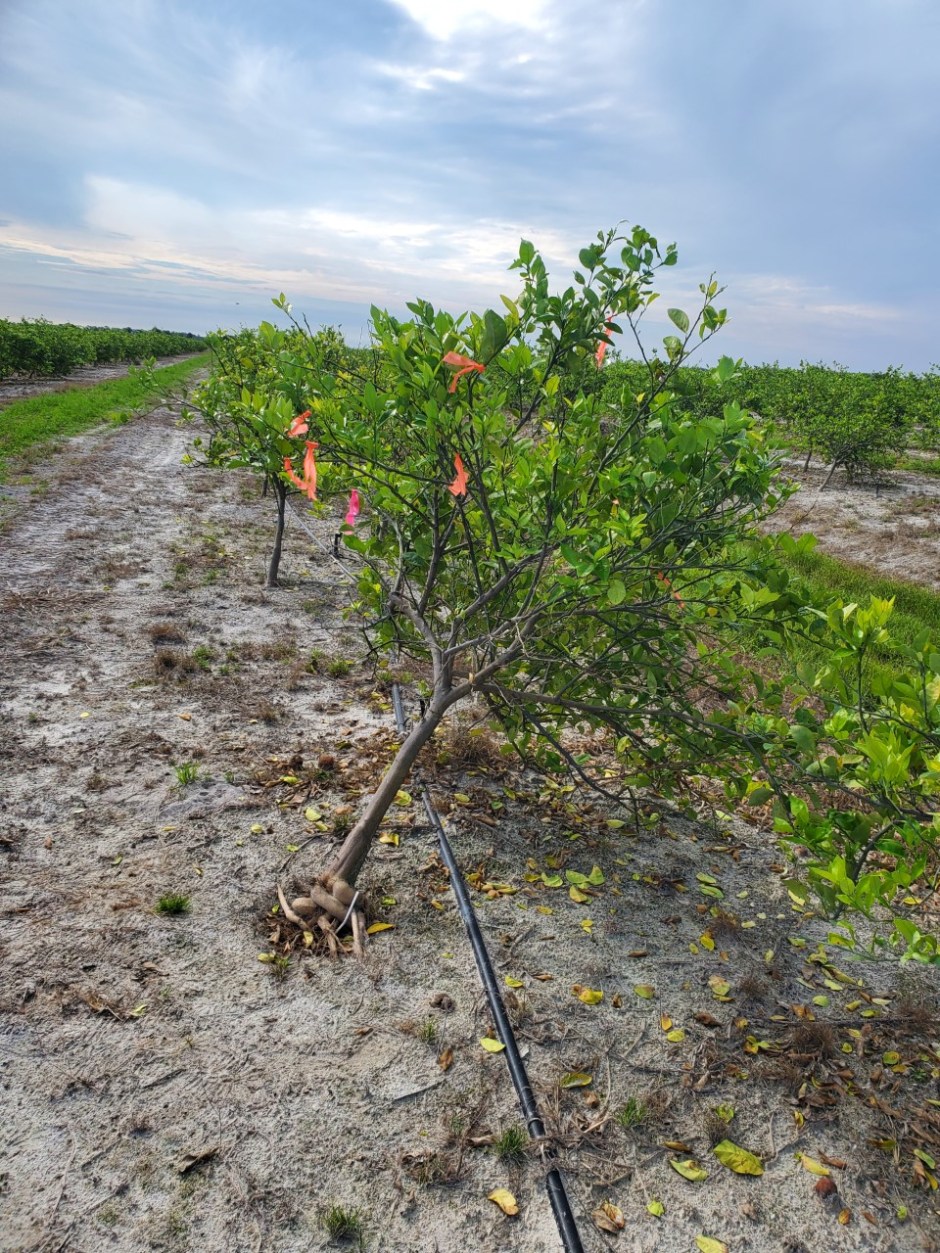
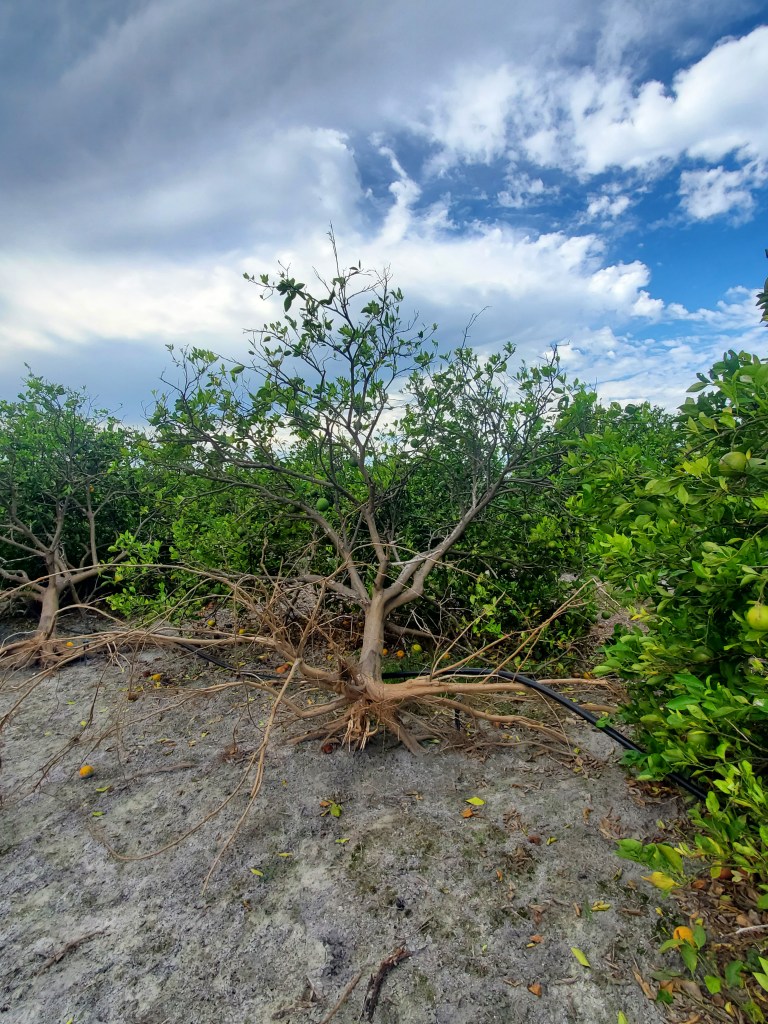
| The windward side of a tree is the side that receives more pressure from wind. The leeward side faces away from the wind. The windward side of the trees affected by the hurricane are taking a longer time to recover than the leeward side. The damage these trees are exhibiting includes canopy loss, and bent and broken branches. Some trees are now at an angle because of the pressure from the wind. |
A damaged tree in Punta Gorda in July 2023.
This graph looks at the effects of the wind on the canopy on the windward side versus the leeward side of the tree.
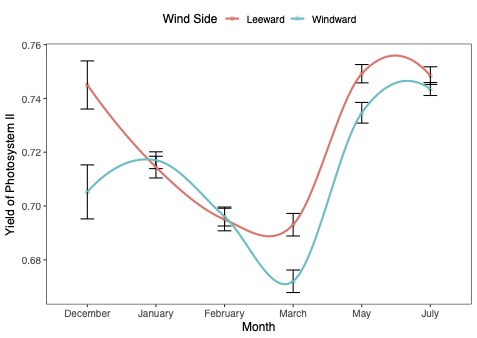
| This figure shows how a measure of leaf health has changed in windward and leeward sides in the same trees since December. Higher values suggest that the trees are healthier and less stressed. Summer weather helped the trees recover, but leaves on branches that directly faced winds during Hurricane Ian have still not caught up with those facing away from the wind. |
| The tree’s ability to transport water is at the heart of how hurricane winds impact citrus trees. Along with a lab in Gainesville, we examined how the intensity of the hurricane-affected the trees’ ability to move water through the stems (xylem functionality). The study looked at locations that had Categories 1 and 3 storms, as well as a site that avoided hurricane-force winds. The area with the weakest intensity had the greatest ability to move water. The area with Category 1 intensity had the worst xylem functionality. The damage at this site did not show immediately, as it had where the winds were Category 3. This helps explain observations by many growers that storm effects are not all immediately obvious. We suspect it is taking the trees so long to recover because spring was dry, making less water available to trees that have a hard time moving water from the soil to the leaves, so the trees have not been getting the moisture they need to support recovery. |
A grove in Zolfo Springs in July 2023.
For questions or more information, please contact project leader Christopher Vincent at civince@ufl.edu.